A healthy diet is not just about weight management; it plays a crucial role in preventing various diseases and promoting overall well-being. As we navigate our busy lives, it’s essential to prioritize our dietary choices to safeguard our health. Let’s delve into why a balanced and nutritious diet matters:
1. Protection Against Malnutrition and Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs)
A **healthy diet** acts as a shield against malnutrition in all its forms, including undernutrition and micronutrient deficiencies. Additionally, it significantly reduces the risk of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) such as:
– Diabetes
– Heart disease
– Stroke
– Certain cancers
2. Global Health Risks: Unhealthy Diet and Physical Inactivity
Unhealthy eating habits and insufficient physical activity are major global health risks. These lifestyle factors contribute significantly to the rise of NCDs worldwide. By making informed dietary choices, we can mitigate these risks.
3. Starting Early: Healthy Dietary Practices for Lifelong Benefits
Healthy dietary practices should begin early in life. For infants, breastfeeding fosters healthy growth, cognitive development, and long-term health benefits—reducing the risk of obesity and NCDs later on.
Key Principles of a Healthy Diet
While individual dietary needs may vary based on factors like age, gender, lifestyle, and cultural context, some fundamental principles remain consistent:
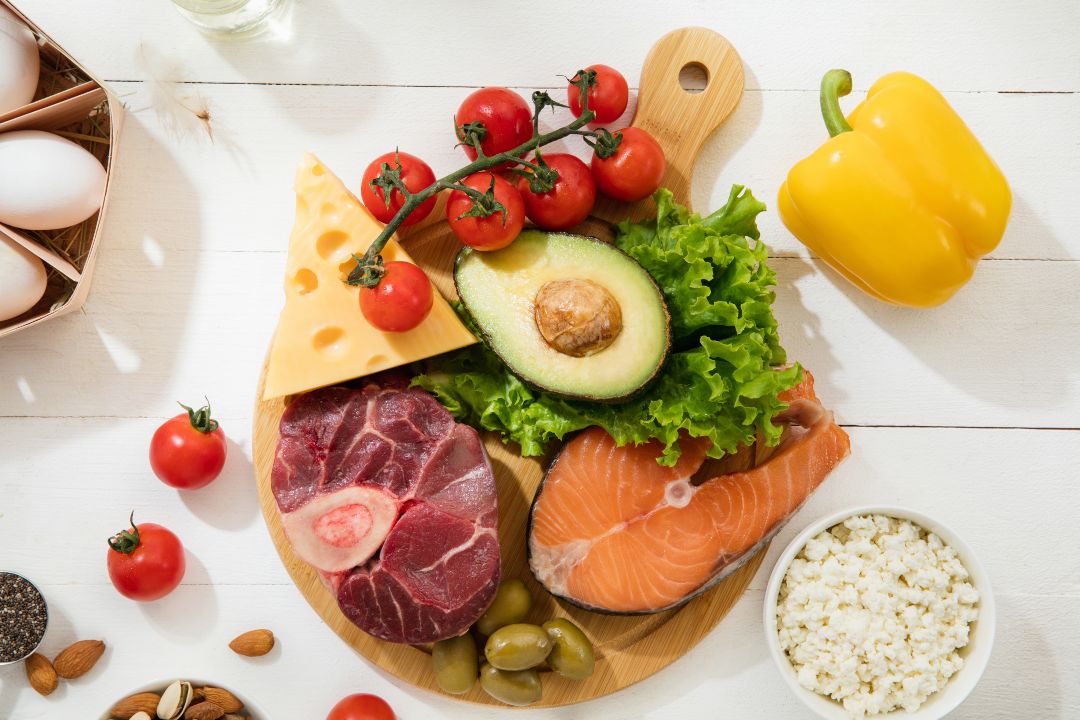
1. Fruits, Vegetables, Legumes, Nuts, and Whole Grains: Aim for at least 400 grams (approximately five portions) of fruits and vegetables daily (excluding starchy roots like potatoes). These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber.
2. Limit Free Sugars: Keep free sugar intake below 10% of total energy intake (equivalent to about 50 grams or 12 teaspoons for an average adult consuming 2000 calories per day). For additional health benefits, strive for less than 5% of total energy from free sugars.
3. Healthy Fats: Total fat should not exceed 30% of total energy intake. Saturated fats should be less than 10%, while trans-fats should be less than 1%. Prioritize unsaturated fats over saturated fats.
4. Salt Intake: Limit daily salt consumption to less than 5 grams (equivalent to less than 2 grams of sodium). This helps prevent hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
The Role of Balanced Nutrition
Balanced nutrition involves variety—choosing foods from different food groups to meet all nutrient requirements. It’s not about extreme restrictions but rather about creating a sustainable eating pattern that nourishes our bodies.
In summary, adopting a balanced and nutritious diet isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s a powerful tool for disease prevention and overall health promotion.
Remember: What you put on your plate today impacts your health tomorrow!











0 Comments